EU Parliament procurement study: “Exempt collective agreements as a general rule”
06.10.23
An EMPL study on the social impact of public procurement highlights the legal uncertainties that limit collective bargaining.

“Respect for collective agreements should never be seen as an anti-discriminatory measure,” highlights the EMPL study on the Social Impact of Public Procurement. This long-needed study finally sheds light on the EU public procurement rules’ legal uncertainties, discretionary irregularity, and insufficient patchwork solutions on ensuring decent work. The study highlights how the Public Procurement Directive’s legal uncertainties limit collective bargaining. The study goes on to recommend that revisions of the public procurement framework should “exempt collective agreements as a general rule.”
Ahead of a public hearing on the social impact of public procurement on 25 October 2023, the organiser, the EMPL committee, has commissioned this study on the same topic.
“The decency of work and respect for the workers voice should not be hanging in a thin line strung from legal uncertainties and opt-out options. The EU should in all its legislation promote collective bargaining in order to reach the target of a collective bargaining coverage rate of 80 per cent as set out in the Directive Adequate Minimum Wages,” said Agnes Jongerius (S&D, the Netherlands), Member of the European Parliament and S&D Coordinator of EMPL.
Legal uncertainty and patchwork solutions
Public contractors need to follow collective agreements. In some countries, this is straightforward as sectoral agreements are applicable to all companies and workers of that sector. But where this is not the case, there is obvious legal uncertainty.
The EMPL study flags the problems of the public procurement directive, the social clause (Article 18(2) of Directive 2014/24/EU) “does not offer sufficient legal clarity when there is no applicable collective agreement.” and that this “may have a chilling effect on contracting authorities wishing to promote collective bargaining in the context of public procurement.
In Malta, contracting authorities that gave extra points as award criteria to companies with company-level collective agreements “have constantly been involved in lawsuits”. This has a chill effect on authorities trying to promote fair competition and good working conditions.
Opt-in/opt-out approach to social responsibility doesn’t work
The study also addresses the inherent shortcomings of the voluntary approach for Member States to ensure that public procurement money is spent in socially just and fair ways: “An important key finding is that the use and correct implementation of SRPP requires, first of all, the willingness from the contracting authorities to use SRPP.”
This opt-in/opt-out approach to the respect for social responsibility is also felt by SME’s who complain about the non-respect of the mandatory social clause by contracting authorities, and that the contracting authorities “award contracts only on the basis of the cheapest offer, thus undermining fair competition with bidders that want to comply with social and labour law.”
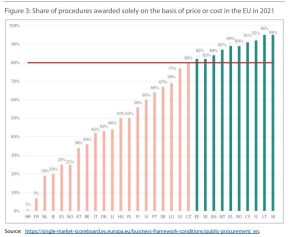
With this laissez-faire approach it probably does not surprise anyone, when the European Parliament report demonstrates that the use of the lowest price is still widespread in the EU. In 2021, 10 Member States awarded 82-95 per cent of their tenders solely on the basis of the lowest price or cost.
Solutions are addressed in the report, which highlights how the Directive on public procurement could “take inspiration from legislation on cartels, which recognises that collective agreements cannot be seen as a discriminatory measure.” It is generally agreed that collective bargaining pursues legitimate objectives in the public interest and should therefore not be seen as breaching competition law. This is further suggested in the recommendations for a future reform of the EU’s public procurement framework.
The study’s recommendations
The European Parliament study among other makes the following recommendations for future reform of the EU’s public procurement framework:
- Revise and clarify the mandatory social clause, by explicitly stating that collective agreements can never be considered a discriminatory measure in public contracts;
- Exempt collective agreements as a general rule from the link to the subject matter, and give Member States the possibility of justifying exceptions to the link to the subject-matter requirement where important social objectives cannot effectively be addressed through measures which are strictly limited to the goods, services or works being purchased;
- Consider developing specific Directives to regulate public procurement in specific sectors, such as in labour-intensive, low-skilled service sectors;
- Strengthen the conditionalities in EU funding related to public procurement.
For UNI Europa, the message is clear. The most effective way forward is a change in the Public Procurement Directive so that there is No Public Contract without Collective Agreement. This is further supported by more than 170 MEPs across five political groups.
Referenced document:
Related articles:
- Over 170 MEPs Call for public contracts to only go to decent employers
- FAQ: Public procurement in Europe must respect and strengthen collective bargaining
- Open Letter: Over 160 MEPs call on EU Commission to fix public procurement directive
- Experts from IMCO/ENVI hearing call out broken public procurement directive
You may also be interested in

Von der Leyen’s public procurement reform must lift workers’ living standards
19.07.24
Press Release
Meetings & Events
2024
10
Sep
Protected: UNI Europa FATIMA Project – 3rd Steering Group Meeting – 10 September 2024
Commerce
ICT & Related Services
Property Services